



In this part we will assume that you have a basic understanding of simple circuits as explained in the Electromagnetism section.
Maths expectations:
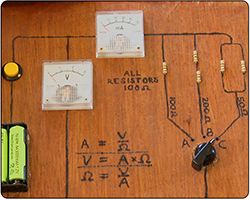 Resistors and Ohm's Law
Resistors and Ohm's Law
When you start on the electronics path, there is no better first step than Ohm's law and so much builds on this theory.
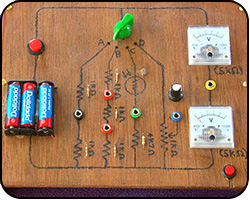
Explained: Ohm's Law, resistance, resistors, Ohms, parallel resistors, resistors in series. Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09a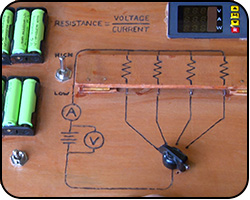 Ohm's Law Practical
Ohm's Law Practical
Here we test out our understanding of Ohm's Law by trying to work out the resistance value of the unknown resistors.
Explained: digital meters, watts.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09a
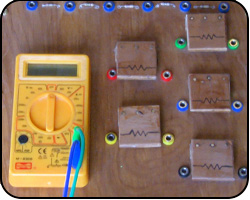 Multi-meters and Resistor Rings
Multi-meters and Resistor Rings
Another board where we try to find the
resistance value of resistors, but this time we have the aid of a multimeter. We also introduce the
rings found on the resistors which gives us the resistance value and their tolerance (how close there are likely to be to the give value).
Explained: multi-meters, resistance ranges, resistor rings, tolerance.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09a
 Potential Dividers
Potential Dividers
Now we look at the voltage across resistors when we have two or more wired together in series.
Explained: potential dividers, light depedant resistors, variable resistors, potentiometer.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09a
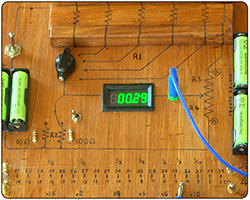
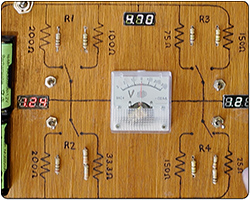 Whetstone Bridge
Whetstone Bridge
This circuit might be nearly two hundred years old, but understanding what it's does and how it does it expands our understanding of potential dividers.
Explained: whetstone bridge, digital voltmeters, switchable resistors, centre point voltmeter, resistance wire.
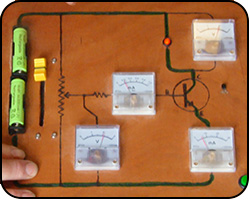 Transistors
Transistors
Transistors have been a main-stay of electronic circuits for well over half a century, here we introduce the basic way of working.
Words explained: transistor, semi-conductor, variable resistor slide potentiometer
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
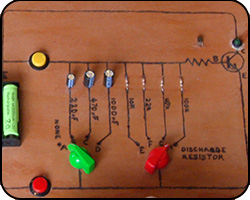 Capacitors
Capacitors
Now we move to capacitors and we look at one of the main uses for this important component.
Explained: capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, discharge resistors.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
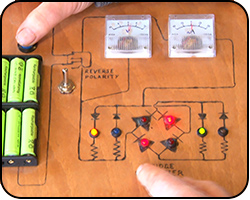 DiodesThese innocent little components are great fun and a bit of light relief after some of the other subjects we have looked at.
Explained: electronic valve, centre point ammeter, reverse polarity, bridge rectifier.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
DiodesThese innocent little components are great fun and a bit of light relief after some of the other subjects we have looked at.
Explained: electronic valve, centre point ammeter, reverse polarity, bridge rectifier.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
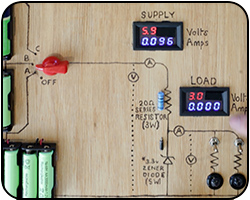 Zener Diodes
While these components are not as used as much as they used to be, it's important we understand them for the occasions when we do come across them.
Words explained: zener diode, load voltage and current, supply voltage and current.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
Zener Diodes
While these components are not as used as much as they used to be, it's important we understand them for the occasions when we do come across them.
Words explained: zener diode, load voltage and current, supply voltage and current.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
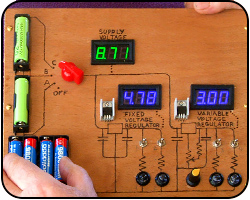 Voltage Regulators
Voltage Regulators
As no modern power supply is complete without one of these, it's important we have a good understanding of what these components are all about.
Explained: fixed voltage regulator, variable voltage regulator.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09b
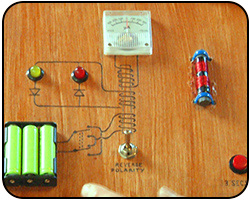 Electromagnetic Induction
While it might look like we are going back to theory explained in the Electromagnetism section, here we refresh our understanding of electromagnetic induction in preparation of the next board.
Explained: electromagnetic induction, ferrite cores, coils.
Electromagnetic Induction
While it might look like we are going back to theory explained in the Electromagnetism section, here we refresh our understanding of electromagnetic induction in preparation of the next board.
Explained: electromagnetic induction, ferrite cores, coils.
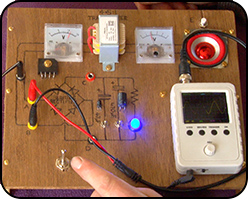 Alternating Current
Alternating Current
Now we really pull together what we have learnt in this section by looking at alternating currents and introduce oscilloscopes and transformers.
Explained: transformer, oscilloscope, smoothing capacitors, speakers, mains hum, hertz, frequency.
 Resistor Capacitors (RC) Circuits
Resistor Capacitors (RC) Circuits
The combination of a resistor and capacitor is used in numerous timing and oscillating circuits - all is explained here.
Explained: RC (resistor capacitors), timing circuits, Exponential curve, charging, discharging
Cur. Ref: SCN 4-09b
 The Astable Flip-flop Multivibrator Transistor Circuit
The Astable Flip-flop Multivibrator Transistor Circuit
Now we really pull together and explore this classic circuit.
Explained: multivibrator, astable, flip-flop, capacitor charging & discharging
Cur. Ref: SCN 4-09c
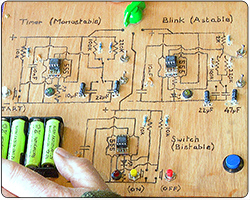 The 555 Timer
The 555 Timer
This is our first intergrated circuit. It's been around over 50 years and is still used in timing circuits so its a great place to start.
Explained: timers, astable, bistable.
Cir. Ref: SCN 4-09c